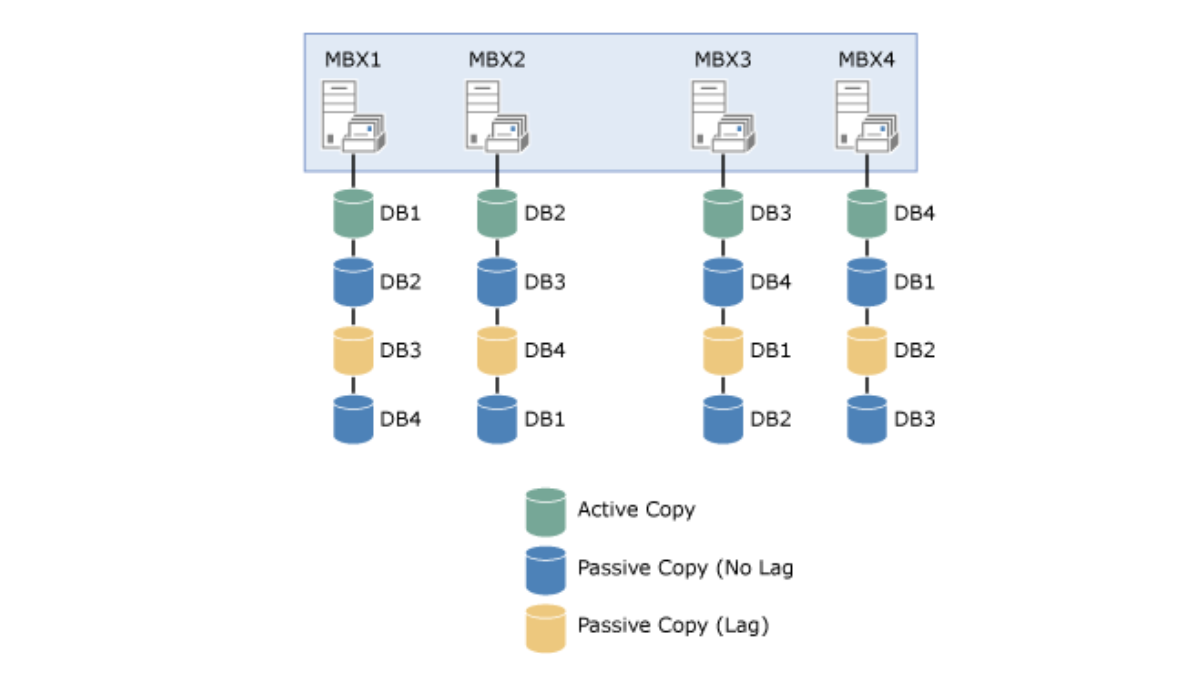
Deploying a database availability group (DAG) in an Exchange Server environment is a critical task for maintaining high availability of Exchange mailbox databases. A DAG provides automatic database-level recovery from database, server, and network failures, and it is the core component of Exchange high availability. In this guide, we will provide a step-by-step process for deploying a DAG in Exchange Server.
Table of Contents
Before we start, it is important to note that this guide assumes that you have already installed and configured Exchange Server. If you have not yet installed and configured Exchange Server, please do so before proceeding.
Understanding DAG
A database availability group (DAG) is a group of up to 16 Exchange mailbox servers that host a set of databases and provide automatic database-level recovery from database, server, and network failures. In other words, a DAG is a group of Exchange servers that work together to provide high availability for mailbox databases.
DAGs are created and managed using the Exchange Administration Center (EAC) or Exchange Management Shell (EMS). When you create a DAG, you must specify a name for the DAG, an IP address for the DAG, and a witness server. The witness server is a non-Exchange server that is used to monitor the database availability group and ensure that it is running properly
Preparing for DAG Deployment
Before you can deploy a database availability group, you must first prepare your Exchange servers. The preparation process involves the following steps:
Step 1: Ensure that your Exchange servers are running the same version and edition of Exchange Server. If you have Exchange Server 2016 or later, you can use the Exchange Server Health Checker to verify that your servers are up to date.
Step 2: Configure static IP addresses for all network adapters on each server. This is necessary to ensure that each server has a unique IP address that can be used to communicate with other servers in the database availability group.
Step 3: Create a separate Active Directory (AD) site for each datacenter that will host database availability group members. This will ensure that each datacenter has its own set of AD site links and that Exchange will use the appropriate site link for database replication.
Step 4: Configure the network infrastructure to ensure that all servers can communicate with each other. This may involve configuring firewalls, load balancers, and other network devices.
Deploying a DAG
Once you have prepared your Exchange servers, you can proceed with deploying a database availability group. The deployment process involves the following steps:
Step 1: Open the Exchange Administration Center (EAC) or Exchange Management Shell (EMS).
Step 2: Click on Servers > Database Availability Groups.
Step 3: Click on New database availability group and provide a name for the database availability group
Step 4: Specify the witness server and witness directory.
Step 5: Add the Exchange servers that you want to include in the database availability group
Step 6: Specify the IP address for the database availability group
Step 7: Click on New to create the database availability group.
Step 8: Add mailbox databases to the DAG. To do this, right-click on the database availability group and select Add Database Copy.
Step 9: Specify the server and mailbox database that you want to add to the database availability group.
Step 10: Click on OK to add the mailbox database to the database availability group.
Step 11: Repeat steps 8-10 for each mailbox database that you want to add to the database availability group.
Step 12: Verify that the database availability group is functioning properly by using the Test-ReplicationHealth cmdlet
Frequently asked questions
What is database availability group in Exchange Server?
It’s a high availability and resilience feature in Exchange Server that provides database-level failover and automatic recovery from server or database failure.
How many Exchange servers do I need for database availability group?
You need at least two Exchange servers, both running the same version and edition of Exchange Server, to deploy database availability group.
How do I add members to the database availability group?
You can add members to the database availability group using Exchange Admin Center (EAC) or Exchange Management Shell (EMS).
How do I test the database availability group ?
You can use Exchange Management Shell (EMS) to test the database availability group. In EMS, you can use the Test-ReplicationHealth cmdlet to test the replication health of the database availability group.
Don’t forget to support us by following us on Google News or Returning to the home page TopicsTalk
Join Telegram and WhatsApp for More updates
Follow us on social media